| Linking
with broadcast automation system |
To send dynamic data via the RDS it's very
useful to link the RDS encoder with your broadcast automation system. This usually results
in a possibility of sending commercials, actual song information, program announcements
and more. Almost any broadcast automation system can be linked with our RDS encoders.
The
link may be either indirect or direct.
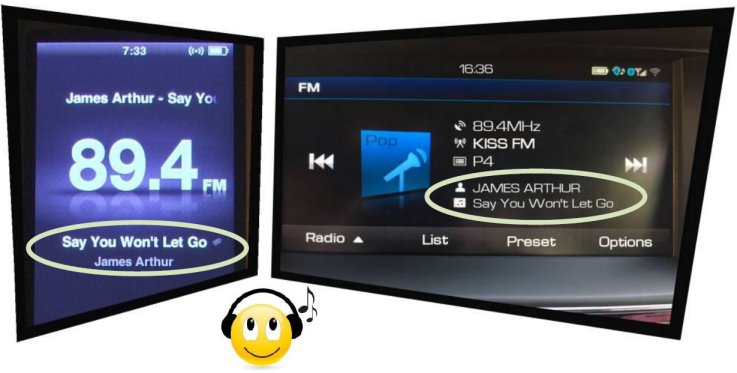
Radiotext Plus (RT+ tagging)
The RT+ feature (also called "tagging") is
designed to let the listener take additional benefit from the Radiotext service by
enabling receivers to offer direct access to specific elements of Radiotext. Typically the
RT+ feature supports song artist and song title elements. These elements anyway carried in
the Radiotext, are identified by their class type, length and location within the
Radiotext.
Our RDS encoders include full support for the RT+
and its handling is highly automated. For direct use your broadcast automation system must
support X-Command or the RT+ function either by means of user defined groups or by the
command RTP=. In other cases the Windows control software used in the indirect link
configuration can provide the RT+ functionality.
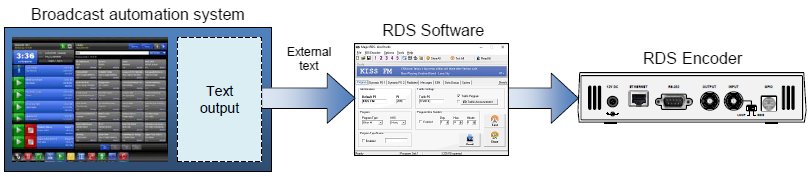
In the indirect link configuration, the broadcast
automation system provides text information usually as a text file. That file is
periodically checked by the RDS encoder's control software and it is sent to the RDS
encoder upon detection of a new text - for example when a new song starts playing.
Default Windows RDS software for our RDS encoders is
the Magic RDS 3. This application, including documentation and examples of use, can be
downloaded in section Software.
We made a pile of work for the linking feature to work with almost any application playing
sound files and providing some relevant text output. Nevertheless broadcast automation
systems with RDS functionality support our RDS encoders directly.
The indirect link configuration may be more
difficult to set-up due to absence of standardized text output across all broadcast
automation systems. On the other hand, this method allows better customization of the
final text and mixing various text sources.
Recommended procedure step-by-step
- Consider the best text output your broadcast
automation system can provide for this purpose. This may be a music log file, now-playing
file, HTTP web file etc.
- Open that file using Windows Notepad to analyze its
structure - how the text desired is saved inside the file.
- In the Magic RDS, enable appropriate text service
(usually Radiotext 1), proceed the Text setup and open the External text tool.
- Enable and configure the Text source in the External
text dialogue box.
As mentioned earlier, the external text source
configuration is different for each broadcast automation system. Since probably hundreds
of automation systems are used around the world and new versions are released often,
information in this document cannot be full-scale. For more information about how to
configure the broadcast automation system text output, please read its documentation or
contact their support. The Magic RDS configuration examples can be found in this guide and in our Technical forum.
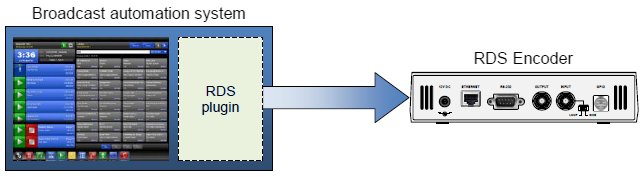
In the direct link configuration, the broadcast
automation system communicates to the RDS encoder without any intermediator.
Recommended procedure step-by-step
- For the present turn off the RDS encoder support in
the broadcast automation system.
- Connect the RDS encoder and configure all basic
parameters like PI, default PS, text setup, enable appropriate text service (usually
Radiotext 1). Use the Windows control software or a terminal application. Store all
setting into EEPROM. Exit the Windows control software or the terminal.
- Find out the baudrate (speed) or network protocol
that is used by the broadcast automation system for communicating with the RDS encoder.
Configure the connection parameters, using Device setup dialogue box or a terminal.
- Turn on the RDS encoder support in the broadcast
automation system.
For more information about how to control the RDS
encoder contact the broadcast automation system vendor or follow our Technical forum.
Data format
RDS encoders from the P132 family support all
relevant data formats (protocols) on all communication ports. Thus they are compatible
with all broadcast automation software which allows direct RDS encoder control. This
applies to TCP communication as well as to connection via serial port or USB.
The data format support includes:
- ASCII commands
- UECP protocol (format given by UECP specification)
- X-Command (not available for PIRA32)
Basic data format for the ASCII command is as
follows:
Prefix (ASCII command): RT1=
Terminating character: <CR> (Carriage return). <CR><LF> accepted
as well.
Example:
RT1=Now Playing: Julia Michaels - Issues¶
See the Technical manual for complete list of all
ASCII commands.
X-Command for RDS encoders
The X-Command is the newest and preferred method how
to forward text information (incl. tagging) from the broadcast automation system to the
RDS encoder. It is based on a simplified markup language. The X-Command is fully supported
by the P132 RDS encoders family and it's supported by all broadcast automation systems
which allow the user to define output data template.
Example:
XCMD=<rds><item><dest>3</dest><text>Now Playing: <artist>Julia Michaels</artist>
- <title>Issues</title></text></item></rds>¶
For more details follow the information in the
document X-Command for RDS Encoders.
|

